SOLENOSTOMIDAE
Ghost pipefishes
By Ukkrit Satapoomin
 Solenostomus paradoxus |
|
|
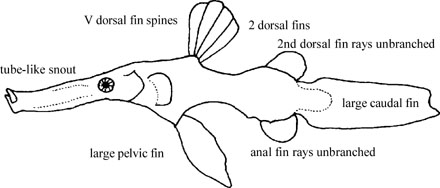
Small fishes, 12 - 16 cm TL; body elongate and compressed with large stellate bony plates that bear spines, variously with cutaneous papillae. Head elongate; snout elongate, tubular, with nasal lamellae; mouth small, toothless, with single mandibular barbel. Two dorsal fins widely separated, each on a raised base, the first with V long weak spines and the second with 17 - 22 unbranched soft rays; anal fin rounded, situated opposite soft dorsal fin and on a raised base, with 17 - 22 unbranched soft rays; caudal fin truncate, rounded, or lanceolate; pectoral fin small; pelvic fins large, situated opposite first dorsal fin, with I spine and 6 soft rays. Lateral line absent. Color: highly variable, ranging between light and dark phases: light color phase with light background often overlain with spots and/or reticulations; dark color phase with overall dusky to black coloration or strongly contrasting reticulations of deep red-brown with yellow to orange spots, lines, or blotches.
Similar families occurring in the area. Aulostomidae: larger; distinct separate dorsal fin spines; lateral line present; never cutaneous papillae. Syngnathidae: body encased in bony ring; no spines in fins; pelvic fins absent; anal fin reduced or absent; brood surface or pouch found in male. Fistulariidae: body depressed rather than compressed; spinous dorsal fin absent; a distinct caudal fin filament present. Remarks. Found over sand or mud bottoms, in seagrass beds, marine algae, or in association with reef vertebrates. Feed on tiny benthic invertebrates and zooplankton. Females with the pelvics forming a brood pouch for incubating eggs. The family name is a combination of Greek, solen = tube, pipe, channel + Greek, stoma = mouth. |
|
|